Skyscrapers, these vast buildings like Burj Khalifa, Taipei 101, Petronas Towers, and Empire State Building, to mention a few, are usually built with traditional raw materials such as steel and concrete. However, there is a new – or should we say old – material emerging in the industry: wood.
Norway has taken the lead at the moment, finalizing an enormous 86-meter skyscraper made in wood. But the race has only just begun.
Generally speaking, steel has resistance, flexibility, and lightness characteristics that are perfectly suitable for skyscrapers.
No traditional natural material can quickly achieve the steel properties once buildings start getting tall.
Constructing high buildings with organic materials such as wood is complex because it is an anisotropic material. A standard wood panel can offer resistance only in one direction, while skyscrapers are tall and flexible buildings stressed from all orders.
However, the monopoly of traditional materials (steel, concrete) generated heavy structures with high construction costs and high environmental impact. The construction sector is responsible for about 40 percent of global energy-related emissions.
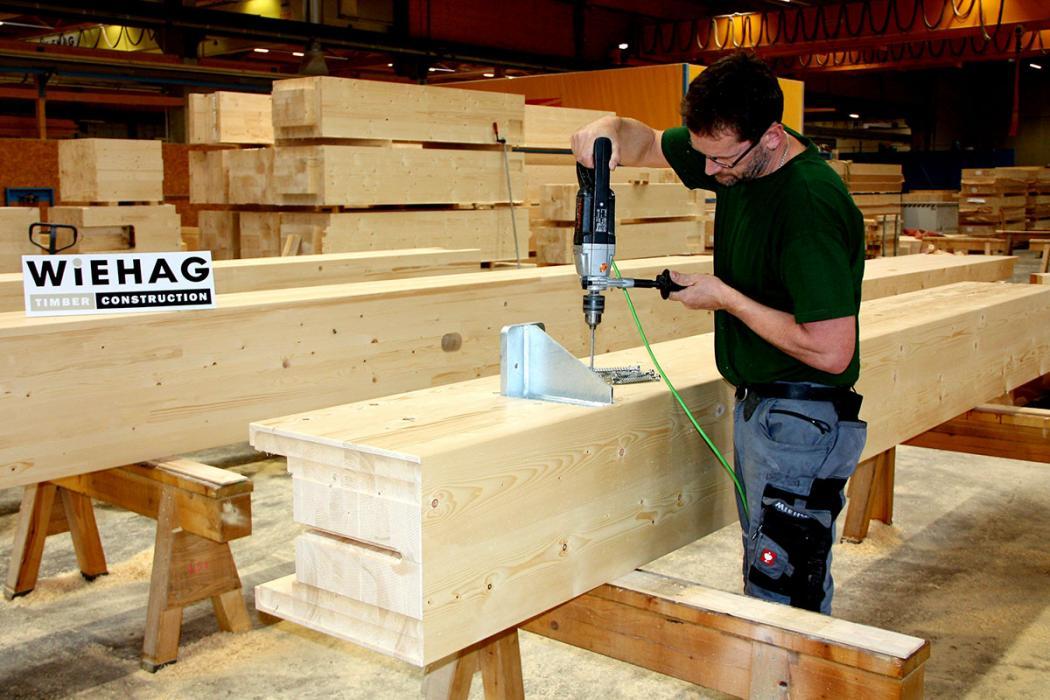

The interest in natural construction materials is on the rise, especially when it comes to wood.
Current research on the technologies CLT (Cross Laminated Timber) and Glulam yield some exciting results for skyscrapers.
So, how do these technologies make feasible what seemed impossible until recently, namely building skyscrapers in wood?
Wooden skyscrapers went further
The wooden skyscrapers were initially an invention of Austria and Germany's Germanic-speaking countries dating back to the end of the twentieth century.
Nowadays, northern Europe is investing a lot of resources in this area. The wooden buildings have repeatedly set height records.
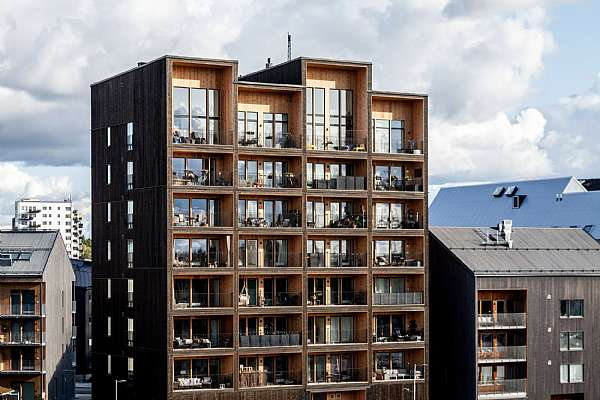

For example, the complex iconically called "The Tall Timber Building" is Sweden's tallest mass timber building.
C.F. Møller Architects designed a 9-story building in wooden CLT and Glulam panels jointed by screws, which means that the structure is demountable and recyclable.
However, the world's tallest skyscraper title belongs to Mjostarnet, an 18-story 85.4 meters (280 feet) high Norwegian building.
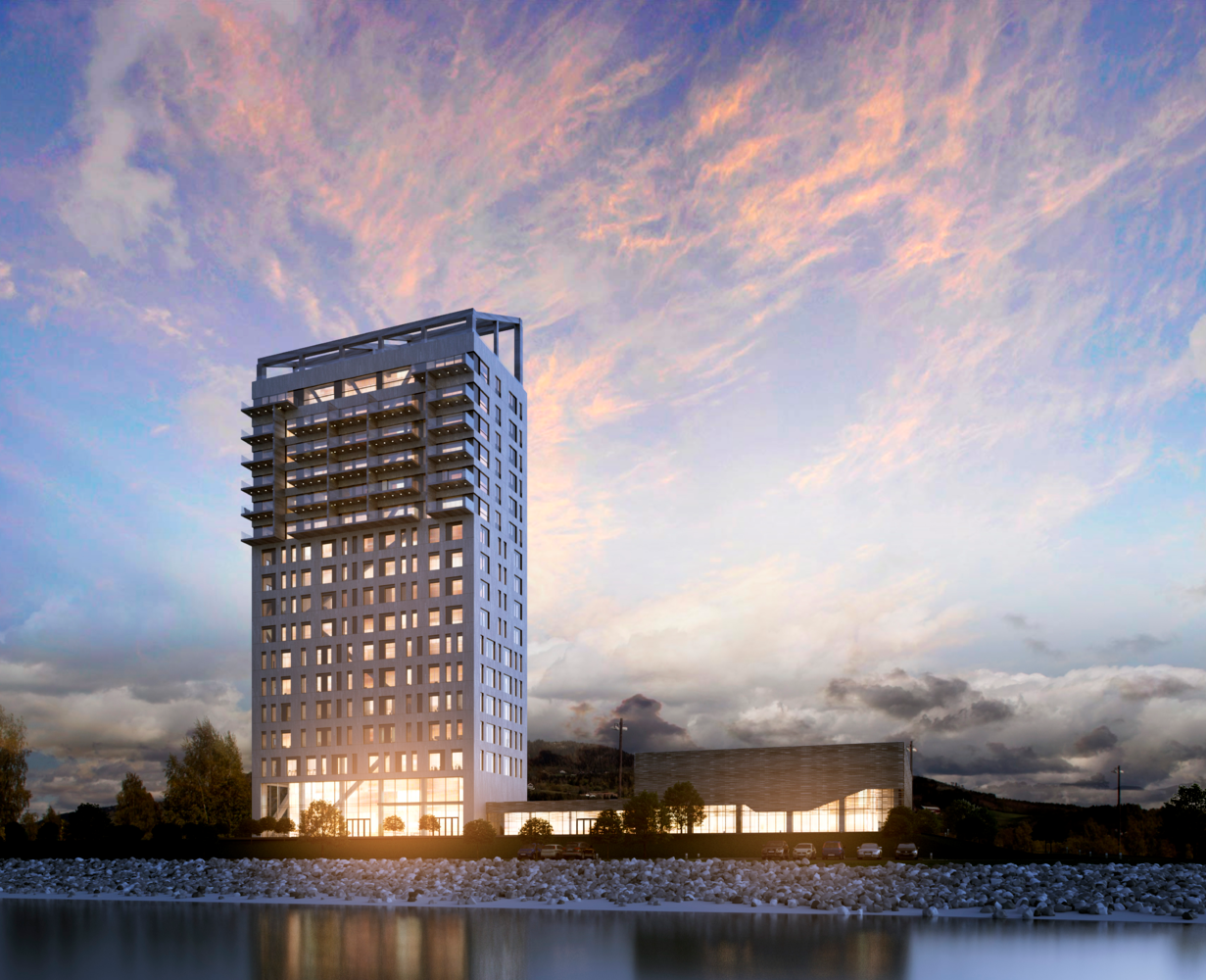

The Moelven Limtre company built the building with columns, beams, and diagonals in CLT laminated wood, while floors and slabs parts are made with Glulam technology.
In this way, a very light structure is created, and it is therefore easy and quick to build. Furthermore, natural materials such as wood help improve human health and well-being through better air quality.
How were these "miracles" technically possible? We need to go inside the wooden houses' structures to understand this properly!
Two technologies that make buildings grow
CLT and Glulam are technologies based on processing the same material, timber lamella glued together, but with different assembling techniques and purposes.
Cross-laminated timber (CLT) technology consists of gluing wooden panels arranged perpendicular to each other. By gluing layers of wood at right angles, the boards achieve better structural rigidity in both directions, overcoming the anisotropy issue.
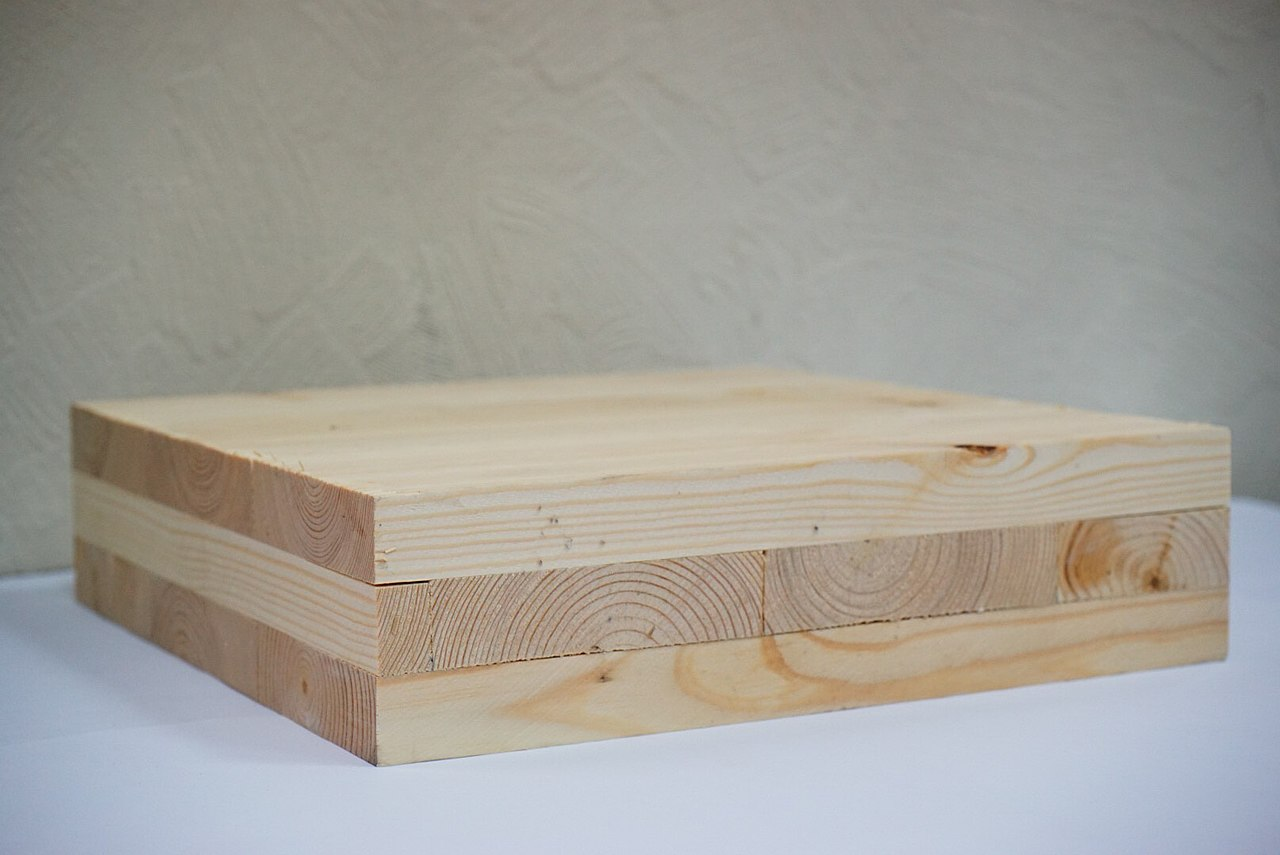

Glulam is made of narrow lamellas all oriented in the same direction, glued, and then pressed together with moisture-resistant structural adhesives. Glulam is stronger and more rigid than solid timber of the same dimension.
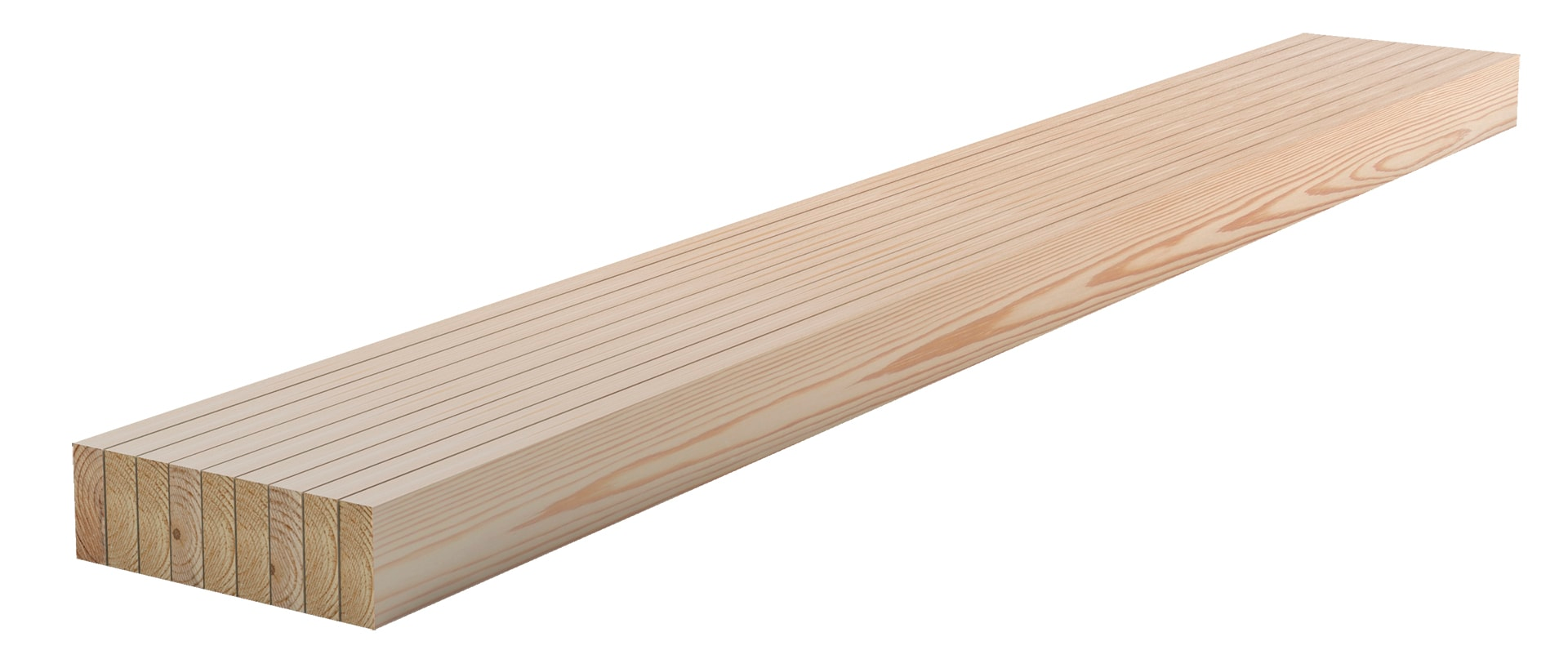

In this way, using Cross-laminated and Glulam panels jointed by screw, it's possible to create a stiff and resistant frame for skyscrapers with a structure similar to those obtainable with steel and concrete elements.
So, this wooden material equals the performances of steel structures, but is it also possible to eventually exceed them and go further?
This is just the beginning…
Several unique possibilities enable excellent prospects for Glulam and CLT timber structures:
- the wood taken from sustainable forests is an eco-sustainable resource naturally absorbing CO2
- at the end of its life, wood can be reused as biomass to produce renewable energy
- the structure has higher thermal and acoustic insulation
- wood is a light and resistant material, allowing creatiothe n of small foundations and reducing transport costs
- …and it has modular and flexible construction elements, lending themselves to prefabricating the elements and assembling them on-site, speeding up construction operations
Not surprisingly, the frontiers of wooden buildiares is already shifting.
Ascent MKE, a 25-story wooden building, 86 meters (284 feet) high, is due to be completed in 2022 in Wisconsin (USA).
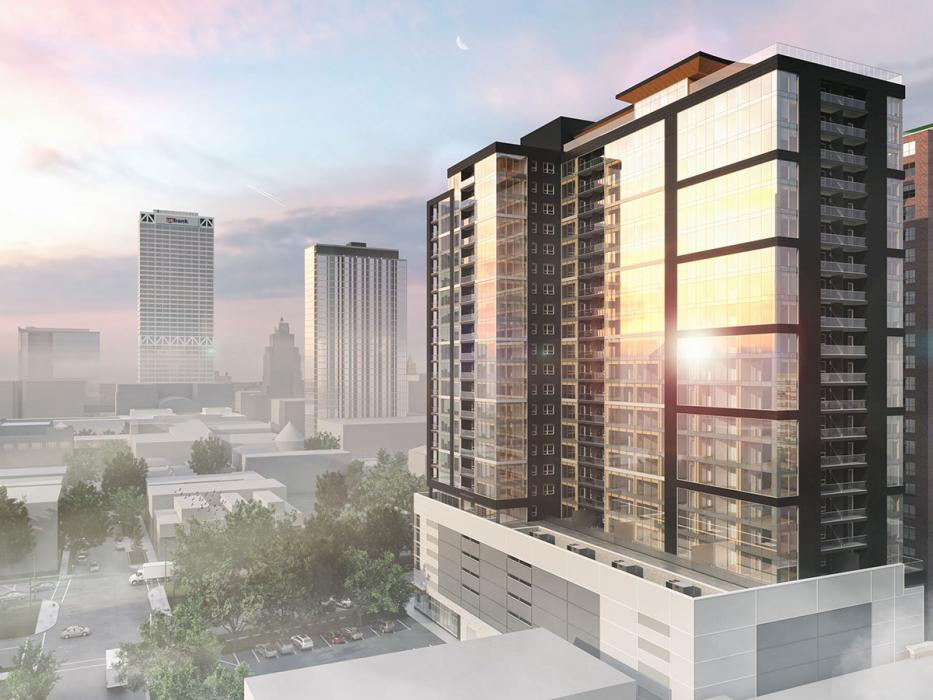

The only limit to these constructions is their low usage, which creates high production costs. But as we have already seen: research is fervent towards saving costs, which are already falling dramatically.
Once these techniques are used extensively, it may become possible to make the wooden skyscrapers even cheaper and further improve the details and technologies to raise the bar for wooden skyscrapers.