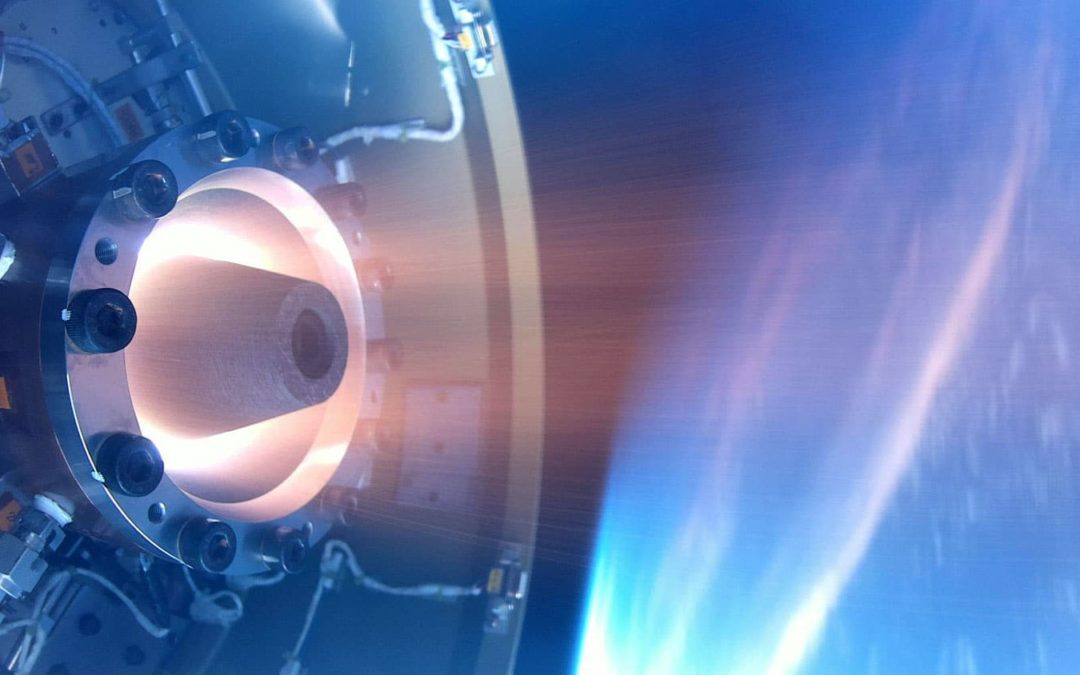
On August 19, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, JAXA, announced that they had successfully tested a Rotating Detonation Engine in space. The launch, which had taken place on July 27, involved a single-stage rocket that carried the experimental engine into space, whereafter it was fired for six seconds before its subsequent return to earth and recovery.
The engine creates spinning explosions using a ring channel to create high thrust using little fuel. The advantage of the engine is that it’s light and efficient, potentially lowering the total weight of a spacecraft, reducing launch costs as well as making it ideal for interplanetary use. Japan isn’t the only country pursuing this technology, but through this launch, they were the first to successfully test it in space.
The engine in question had quite modest performance, only 500 Newtons of thrust. According to Jiro Kasahara, a professor at Nagoya University who worked on the engine, Japan hopes to have operational versions of the engine in five years.